Key Takeaways:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is an evidence-based approach for managing anxiety.
- Understanding how CBT works can help reduce symptoms and improve quality of life.
- Utilizing CBT techniques can offer practical and actionable steps for anxiety relief.
Introduction to Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Anxiety
Anxiety disorders are among the most common mental health challenges faced today. Cognitive behavioral therapy NYC is a well-established treatment that has been proven effective for managing anxiety symptoms. This article delves into practical strategies and techniques within CBT that can help individuals cope with anxiety.
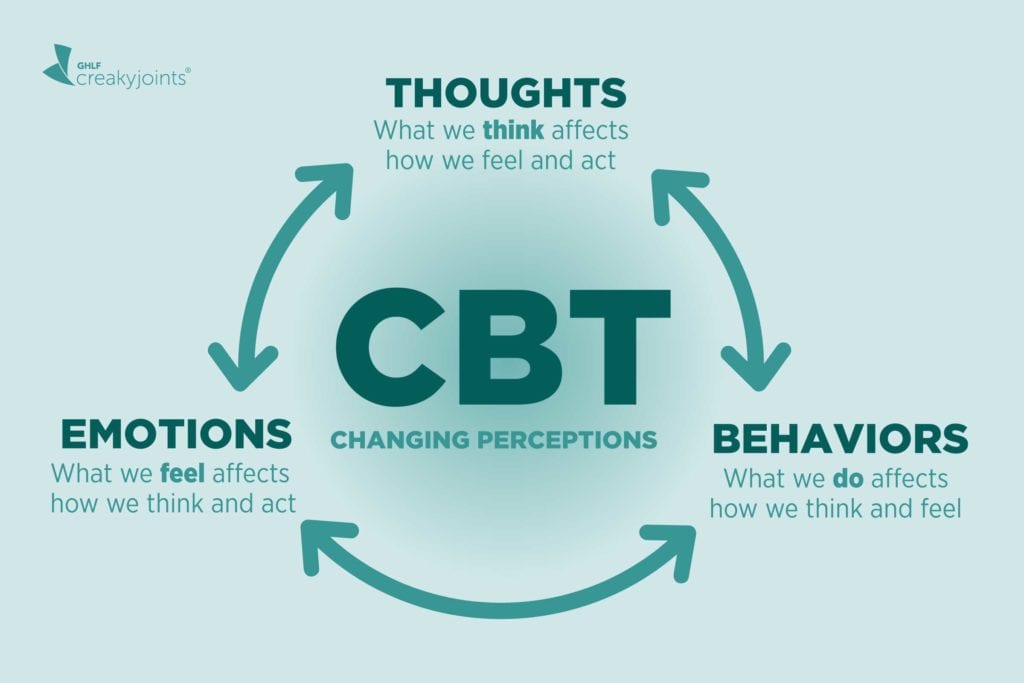
CBT is not confined to a specific location; it’s a globally recognized approach therapists use to help patients restructure their thought patterns. By adopting the principles of CBT, individuals can transform their mental habits, driving away anxiety and welcoming mental peace.
Understanding Cognitive Behavioral Therapy: An Overview
CBT is a form of psychotherapy that focuses on identifying and altering negative thought patterns and behaviors. Its core principle is that our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are interconnected; changing negative thoughts can lead to changes in emotions and behaviors. Research has shown that CBT is highly effective in treating anxiety disorders. CBT can provide significant relief for those struggling with anxiety.
Identifying Negative Thought Patterns
The first step in CBT is recognizing negative thoughts that contribute to anxiety. These thoughts often manifest as irrational fears, overgeneralizations, and catastrophizing. For instance, someone might think, “I’ll never get this right,” which is an example of black-and-white thinking. By identifying these patterns, individuals can start to challenge and change them. This step is crucial as it lays the foundation for further cognitive restructuring. It’s about becoming aware of the automatic negative thoughts that pop into our minds and learning to catch them when they occur.
Challenging and Reframing Thoughts
Once negative thought patterns are identified, the next step is to challenge and reframe them. This involves questioning their validity and replacing them with more balanced, realistic ones. For example, if someone constantly worries about failing at work, they can challenge this by recalling past successes and acknowledging the skills they possess. By doing so, they reframe their thoughts to be more positive and realistic, diminishing the power of their anxiety.
Questioning Thought Validity
To challenge negative thoughts, one needs to ask themselves several key questions. These questions can help dissect and rationalize thoughts, moving from an emotional to a more logical perspective:
- What evidence do I have that supports this thought? This will help me determine whether there is any factual basis for the thought.
- What evidence do I have that contradicts this thought? This allows the mind to see the thought from a different perspective.
- Is this thought based on facts or feelings? Often, anxious thoughts are based more on feelings rather than objective reality.
- What would I tell a friend who had this thought? Thinking about advising a friend helps me see the scenario more clearly and less biasedly.
This systematic approach helps individuals transition from negative to positive thinking patterns, which can significantly reduce anxiety.
Behavioral Techniques for Managing Anxiety
In addition to cognitive techniques, CBT includes behavioral strategies that help individuals face their fears and build resilience. Behavioral techniques are practical activities that help change harmful behavior patterns. This can include exposure therapy, where individuals gradually face anxiety-inducing situations in a controlled manner, and relaxation techniques like deep breathing and progressive muscle relaxation. Behavioral changes often make cognitive changes more sustainable because they reinforce new, healthier ways of thinking.
Exposure Therapy
Exposure therapy is a critical component of CBT. This technique involves gradually exposing individuals to feared situations, helping them build the confidence to face anxiety triggers without avoidance. Over time, this reduces the intensity of the anxiety response. For example, a person afraid of social situations might start by imagining a social setting, then progress to attending a small gathering, and eventually participate in more significant events. Each step is taken at a comfortable pace, ensuring that the individual feels safe and supported throughout the process.
Relaxation Techniques
Relaxation techniques like deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and mindfulness meditation are beneficial in managing the physical symptoms of anxiety. These practices help calm the nervous system and reduce the stress hormones in the body. Deep breathing, for instance, involves inhaling deeply through the nose, holding the breath for a few seconds, and then exhaling slowly through the mouth. This can be repeated several times to induce a state of calm. Progressive muscle relaxation involves tensing and relaxing different muscle groups, which can help reduce physical tension and anxiety.
Practical CBT Exercises for Daily Life
There are several practical CBT exercises that individuals can incorporate into their daily routine to manage anxiety and improve mental health:
- Thought Records: Keeping a diary to track negative thoughts and the context in which they occur can help identify patterns and triggers. By documenting thoughts, individuals can later analyze and reframe them, leading to a decrease in anxiety.
- Activity Scheduling: Planning enjoyable activities can reduce anxiety by providing positive experiences and reducing avoidance behaviors. Engaging in hobbies or activities that bring joy can distract from anxious thoughts and improve overall well-being.
- Mindfulness Meditation: Practicing mindfulness can help individuals stay present and reduce the focus on anxious thoughts. Mindfulness involves paying attention to the present moment without judgment, which can break the cycle of worry and rumination.
Seeking Professional Help
While self-help techniques can be beneficial, seeking help from a professional therapist can provide additional support and guidance. A qualified therapist can tailor CBT techniques to an individual’s specific needs and ensure they are applied effectively. Therapy sessions offer a safe space to explore thoughts and feelings and develop personalized strategies for managing anxiety. Moreover, consistent therapeutic intervention can lead to better outcomes and long-term relief from anxiety disorders.
Conclusion
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy offers a range of practical strategies for managing anxiety. By understanding and applying these techniques, individuals can significantly improve their mental health and overall well-being. Remember, anxiety management is a journey, and utilizing CBT is a decisive step toward a calmer, more balanced life. Making an effort to incorporate CBT techniques into daily life can lead to lasting positive changes, helping individuals live a life free from the constraints of anxiety.

Asad Arshad, a prolific author of over 50+ websites across various niches, is open to collaboration opportunities. 🌐 For guest posts, reach out to him to benefit from his vast expertise and connect with a diverse audience. 📬