Key Takeaways
- Prospective participants must comprehend the processes involved in clinical studies.
- Informed consent and ethical guidelines protect participant welfare.
- The advantages and any hazards should be disclosed to participants.
- Clinical trials contribute significantly to medical advancements.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Phases of Clinical Trials
- Importance of Informed Consent
- Ethics and Regulations
- Potential Risks and Benefits
- Role in Medical Advancements
- Conclusion
Clinical trials are structured studies that evaluate new medical treatments, therapies, or devices to determine their safety and effectiveness. Participants should understand the phases of clinical trials, ranging from initial safety assessments to large-scale efficacy studies. Informed consent is crucial, ensuring participants know potential risks and benefits. Participants may undergo tests and follow-ups, contributing valuable data to medical research. Even though there could be risks, taking part could give you access to cutting-edge medical knowledge and treatments. It’s important to ask questions and fully understand the trial before committing to ensure a positive and informed experience.
Introduction
One essential step in the medical research process is conducting clinical trials. These trials provide crucial data on the safety and efficacy of new treatments. Understanding the nuances of clinical trials is essential for potential participants to make informed decisions. Moreover, clinical trials are vital in improving clinical trial disclosure and transparency, ensuring all stakeholders are well-informed. Due to the improved transparency, more people may be inspired to participate in these crucial research efforts.
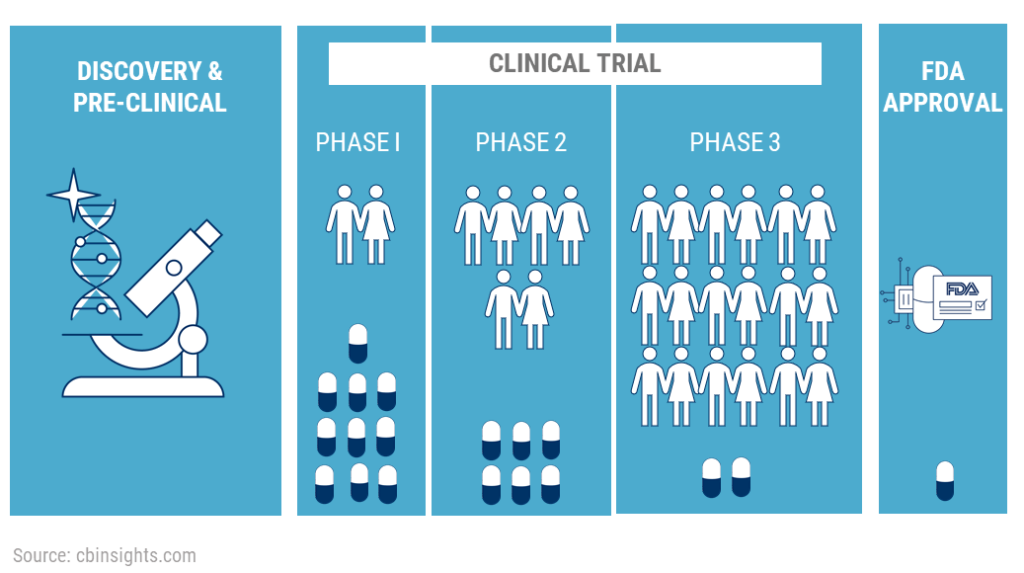
Phases of Clinical Trials
Clinical trials are carried out in several stages, each with a distinct function. Here’s a breakdown:
Phase I
Focuses on safety and dosage. Small groups of healthy volunteers or patients receive the treatment to determine a safe dosage range and identify side effects. Typically, 20 to 80 people participate in this initial phase. The main goal is to analyze how the body reacts to the drug, focusing on the safe dosage levels and noting any side effects.
Phase II
This phase evaluates the treatment’s effectiveness. A larger group receives the treatment, and researchers collect preliminary data on its effectiveness. This phase usually involves several hundred patients. While continuing to evaluate the drug’s safety, the main goal is to ascertain if it effectively treats a particular disease or condition in those with it.
Phase III
This phase involves a larger participant group confirming efficacy and monitoring side effects. It ensures the treatment’s overall benefit-risk relationship is favorable. Thousands of participants may be involved at this stage, often including a diverse population to confirm the treatment’s efficacy across different demographics and gather comprehensive safety data.
Phase IV
They were conducted after FDA approval. This phase gathers additional information on the drug’s effects in various populations and any long-term side effects. Known as post-marketing surveillance, Phase IV trials monitor the treatment’s long-term effectiveness and impact on a broader audience.
Importance of Informed Consent
Informed consent is a fundamental aspect of clinical trials, ensuring that participants fully know their involvement before agreeing to participate. This process involves comprehensive documentation and discussions between the research team and the participant, outlining the trial’s purpose, procedures, potential risks, benefits, and alternatives. It empowers participants to make an informed decision about their participation, considering the possible advantages and the risks involved.
Importantly, informed consent is not merely a one-time formality but an ongoing process. Throughout the trial, participants are regularly updated on new findings, potential side effects, or any changes to the study that may impact their health or the trial’s course. This continuous communication ensures that participants can reassess their decision to stay involved, maintaining their autonomy and safety.
Ethics and Regulations
The ethical and regulatory framework governing clinical trials is designed to protect participants. Guidelines from bodies such as the FDA and the World Health Organization set standards to ensure the safety and rights of participants are upheld. These guidelines require that clinical trials are designed and conducted following specific ethical principles, including respect for persons, beneficence, and justice. Moreover, Institutional Review Boards (IRBs) or ethics committees review the trial protocols to ensure participant safety and ethical treatment.
Potential Risks and Benefits
Clinical trials have the potential to be risky, but they can also provide access to novel medicines. Participants need to weigh these factors before enrolling. Benefits can include contributing to medical advancements and gaining access to cutting-edge treatments, but risks, such as unforeseen side effects, should also be considered. Participants might experience side effects that range from mild to severe, and there might be instances where the treatment does not produce the desired outcomes. However, the hope of improving one’s health and the knowledge they contribute to scientific progress can be compelling motivators for many individuals.
Role in Medical Advancements
Clinical trials are indispensable in developing new treatments that can improve patient outcomes. With the willingness of participants, advancements in medicine would be significantly expanded. Success stories abound, highlighting these trials’ positive impact on areas like cancer treatment and chronic disease management. For instance, groundbreaking therapies for various types of cancer, HIV/AIDS, and multiple sclerosis have arisen from extensive clinical trials. The continuous evolution of medical treatments relies heavily on data garnered from these trials.
Conclusion
Participating in clinical trials is a significant decision with opportunities and responsibilities. Individuals can make well-informed choices by understanding the phases, the necessity of informed consent, and the ethical considerations. Ultimately, clinical trials pave the way for medical breakthroughs and provide hope for future generations. The collaboration among researchers, participants, and institutions fosters a robust environment for scientific innovation, ensuring that treatments evolve and improve over time.

Asad Arshad, a prolific author of over 50+ websites across various niches, is open to collaboration opportunities. 🌐 For guest posts, reach out to him to benefit from his vast expertise and connect with a diverse audience. 📬